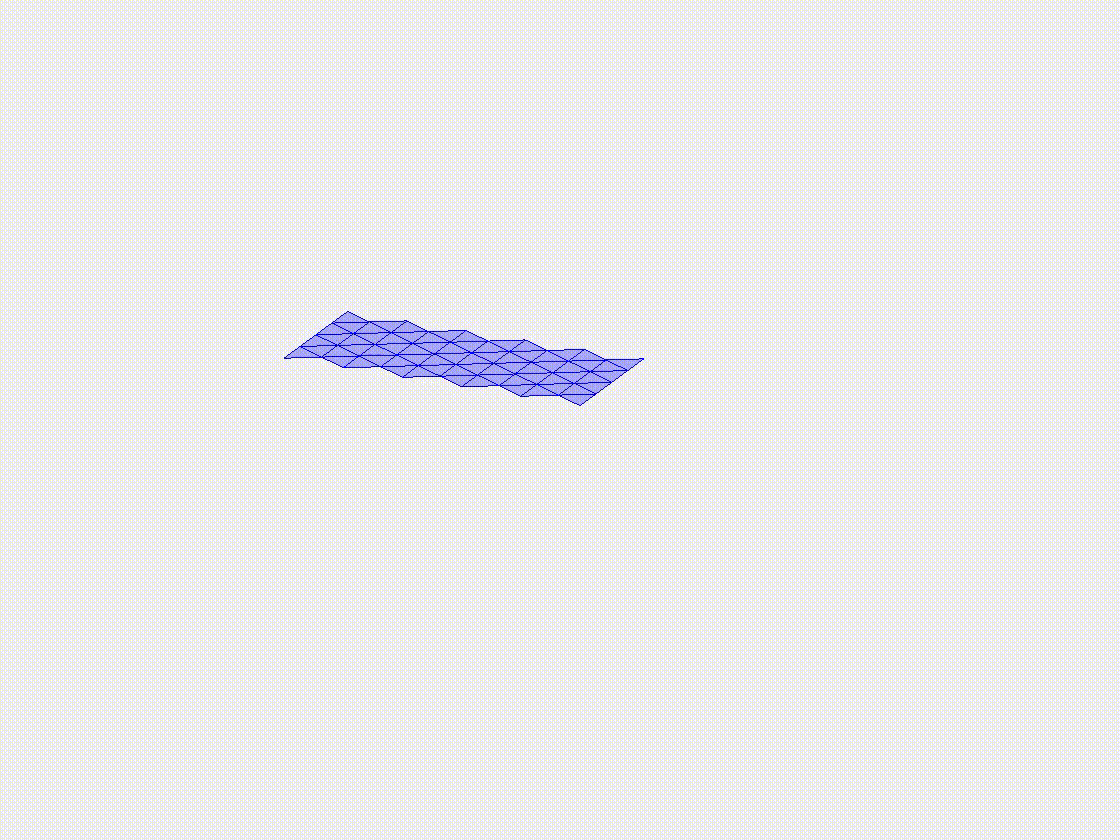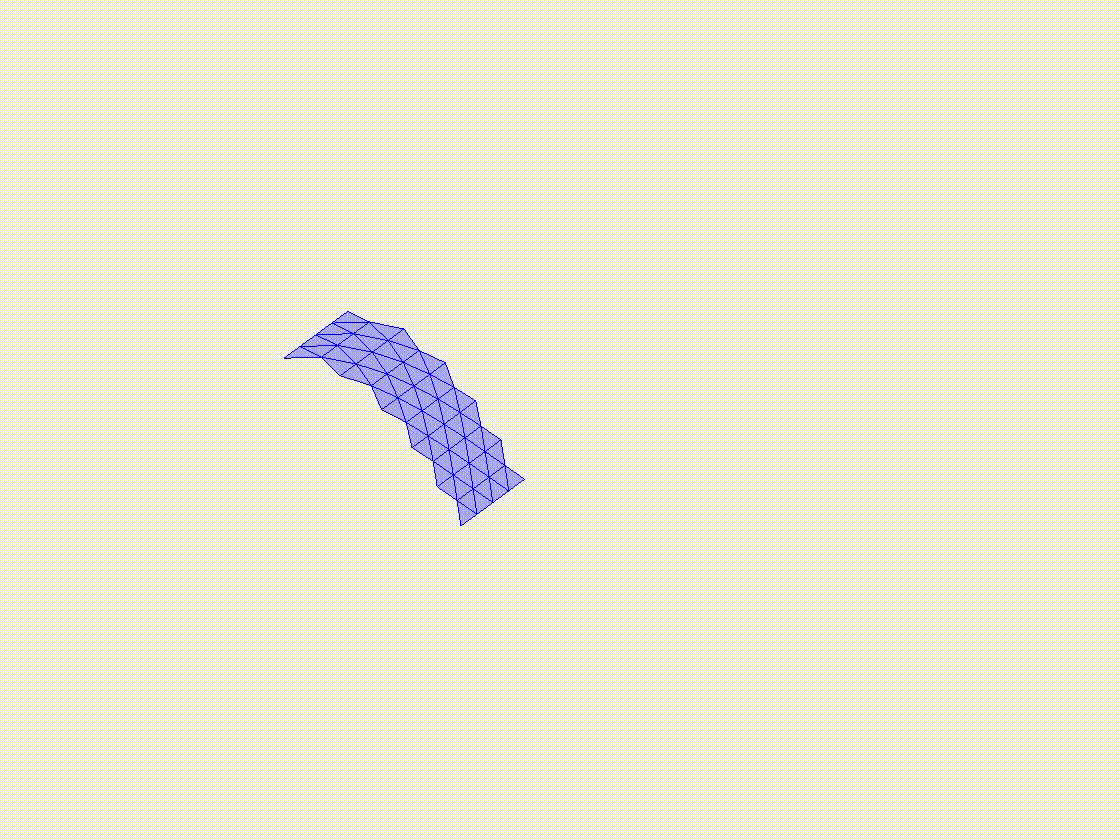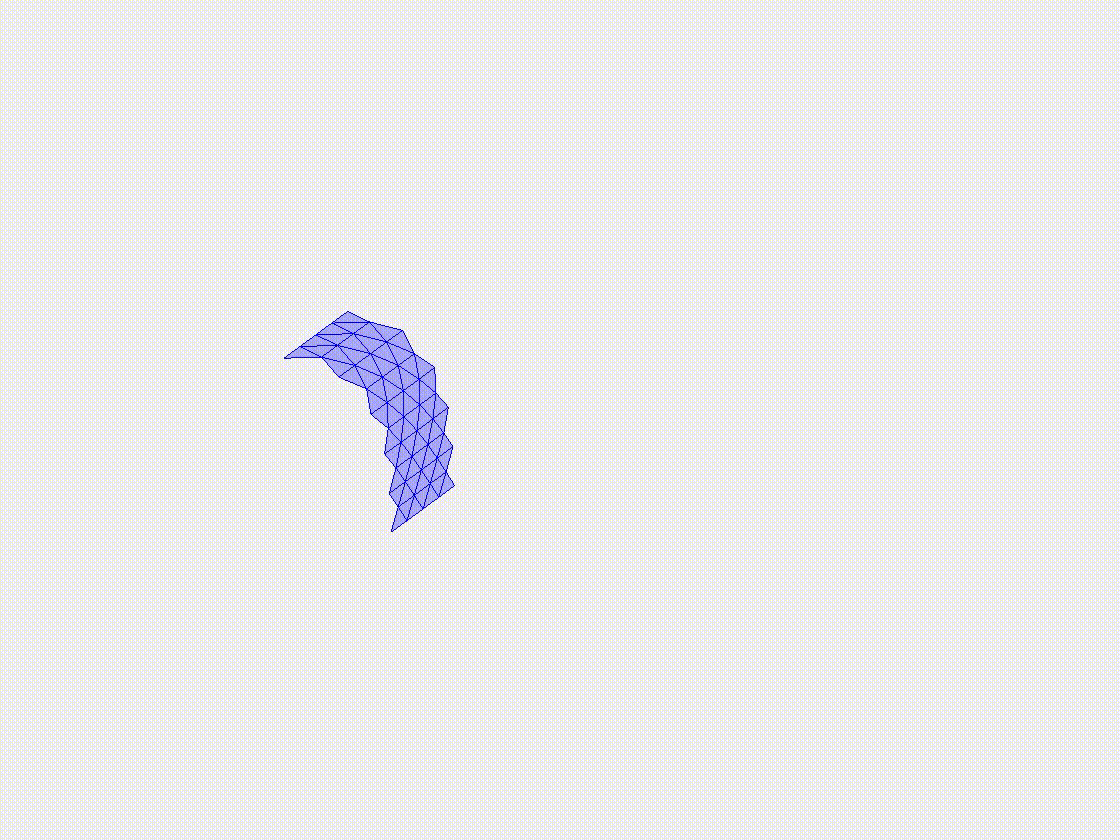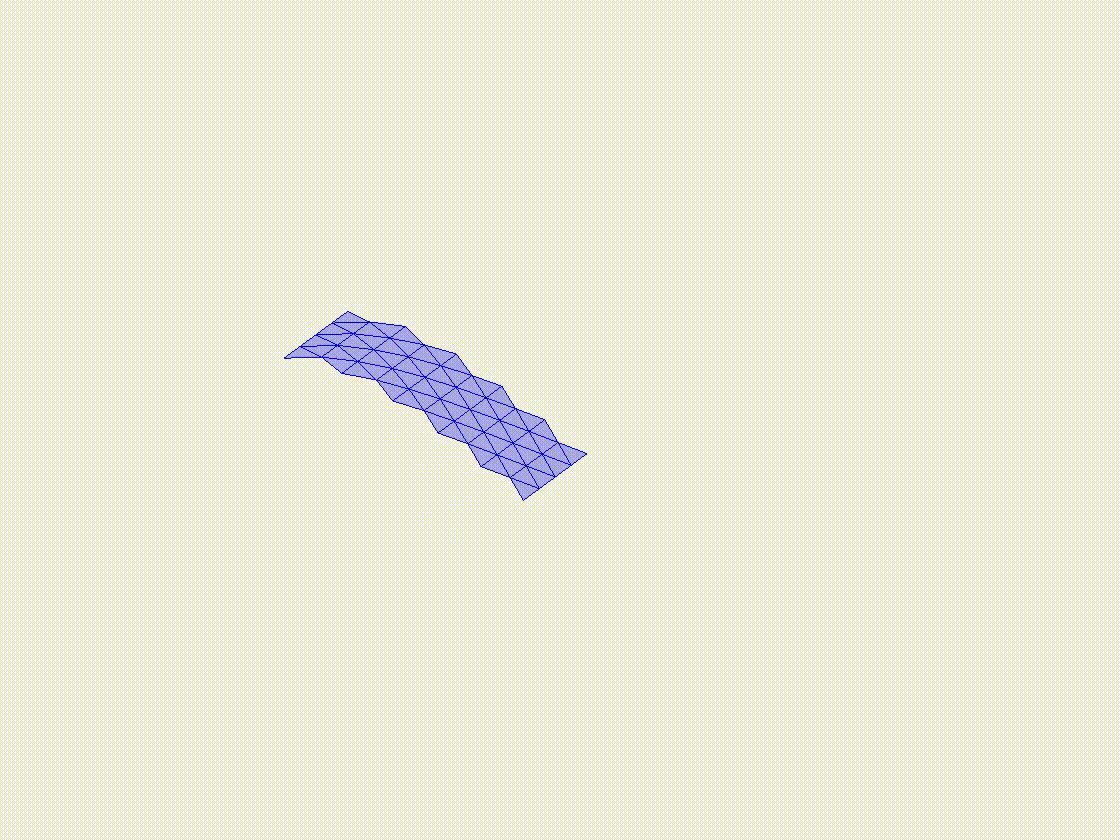
Plate deflection under gravity
In this case study, we examine the deflection of a flexible plate under the influence of gravity. The plate is modeled with clamped-free boundary conditions, with the gravitational load applied uniformly across its surface. The case highlights the ability of the DDG model to accurately simulate the deflection and bending behavior of the plate, providing a basis for more complex simulations involving intricate geometries and varying loading conditions.
Simulation Initialization
To initialize the simulation, the following inputs are used:
- Geometry and connection:
- (i) Nodal positions: the position of the nodes, \(\mathbf{q}(t=0)\), with a total of \(N=50\), with the plate length \(L=1.0\mathrm{~m}\) and width \(W=0.4\mathrm{~m}\).
- (ii) Stretching elements: connection of every two consecutive nodes, with a total of \(N_{s}=119\).
- (iii) Triangular mesh, total number \(N_{t}=70\).
- (iv) Bending elements: connection of every two triangular meshes, with a total of \(N_{b}=91\).
- Physical parameters:
- (i) Young’s modulus, \(E=100\mathrm{~MPa}\).
- (ii) Material density, \(\rho=1000\mathrm{~kg/m^3}\).
- (iii) Plate thickness, \(h = 0.01\mathrm{~m}\).
- (iv) Gravitational field, \(\mathbf{g}=[0.0, 0.0, -10.0]^T \mathrm{~m/s^2}\).
- (v) Damping viscosity, \(\mu = 0.1\).
- (vi) The overall simulation is dynamic, i.e., \(\mathrm{ifStatic} = 0\).
- Numerical parameters:
- (i) Total simulation time, \(T=5.0\mathrm{~s}\).
- (ii) Time step size, \(\mathrm{dt} =0.01\mathrm{~s}\).
- (iii) Numerical tolerance, \(\mathrm{tol} = 1 \times 10^{-4}\).
- (iv) Maximum iterations, \(N_{\mathrm{iter}} = 10\).
- Boundary conditions:
- The first two rows of nodes are fixed to achieve a clamped-free boundary condition, thus, the constrained array, \(\mathcal{FIX}\) can be constructed accordingly.
- Initial conditions:
- (i) Initial position is input from the nodal positions.
- (ii) Initial velocity is set to zeros for all nodes; thus, the constrained array, \(\mathcal{FIX}\), can be constructed accordingly.
- Loading steps:
- External gravitational force is applied to each node throughout the simulation.
Dynamic Rendering