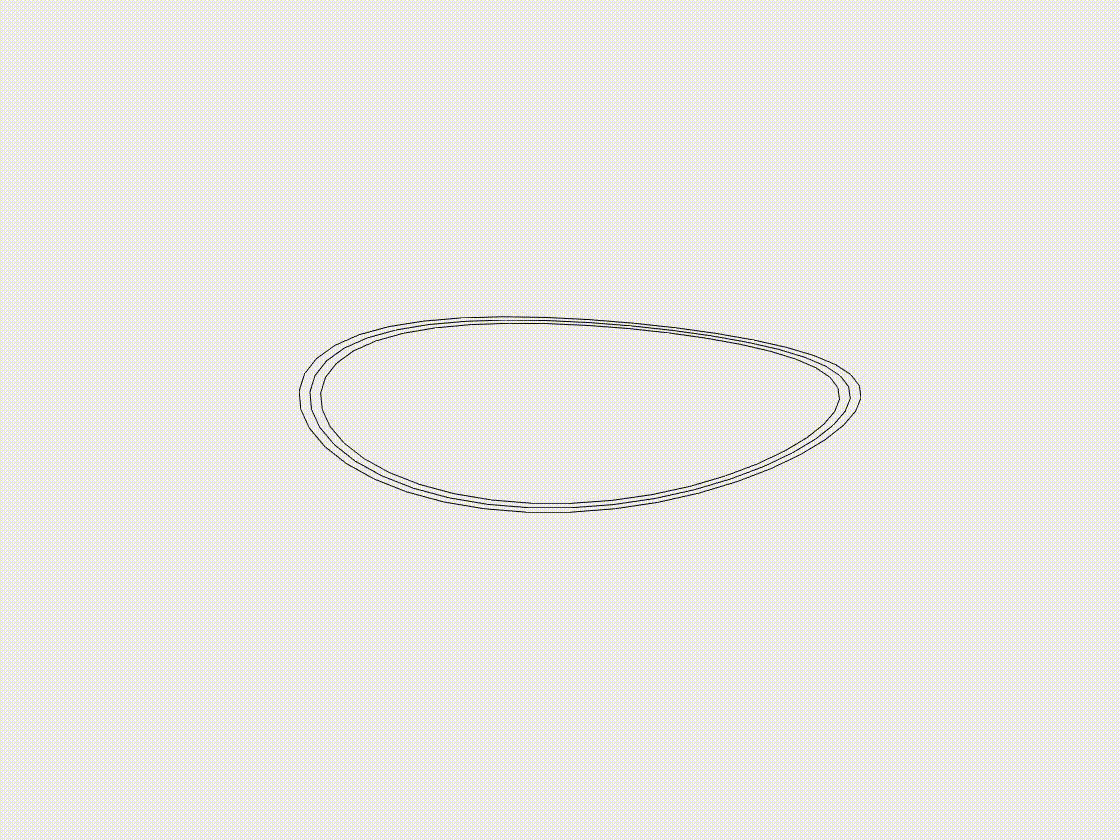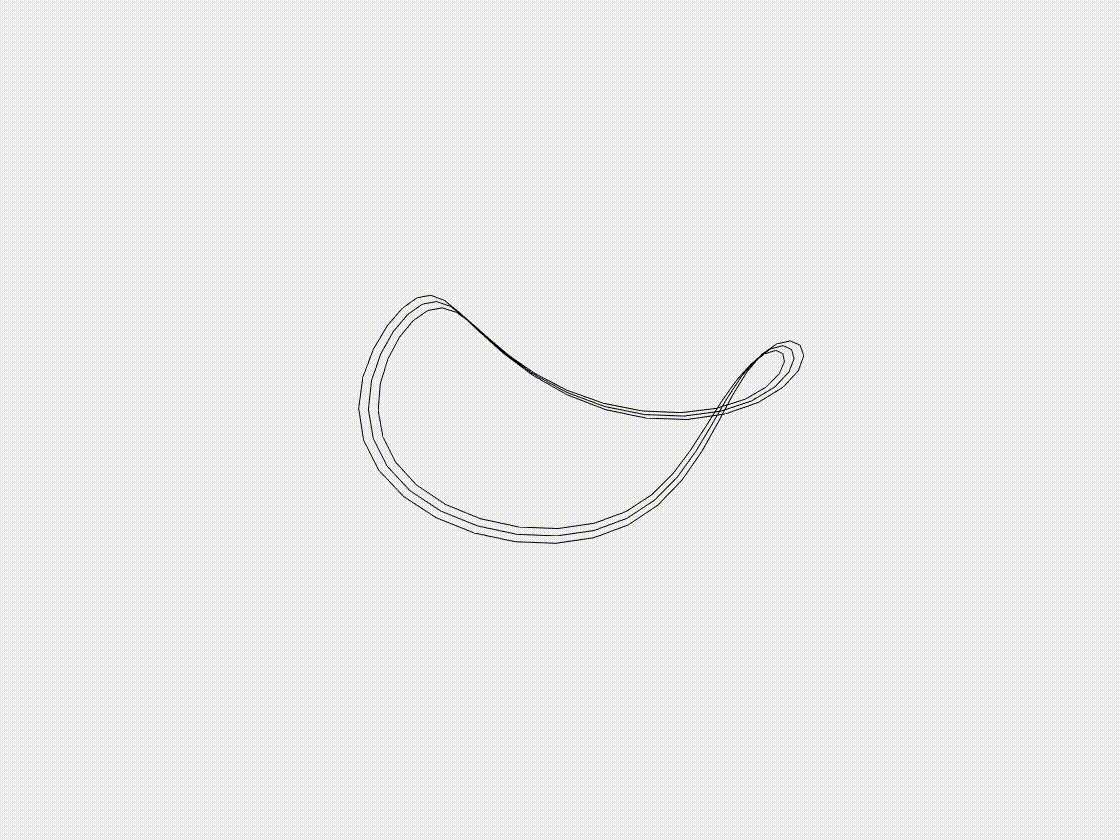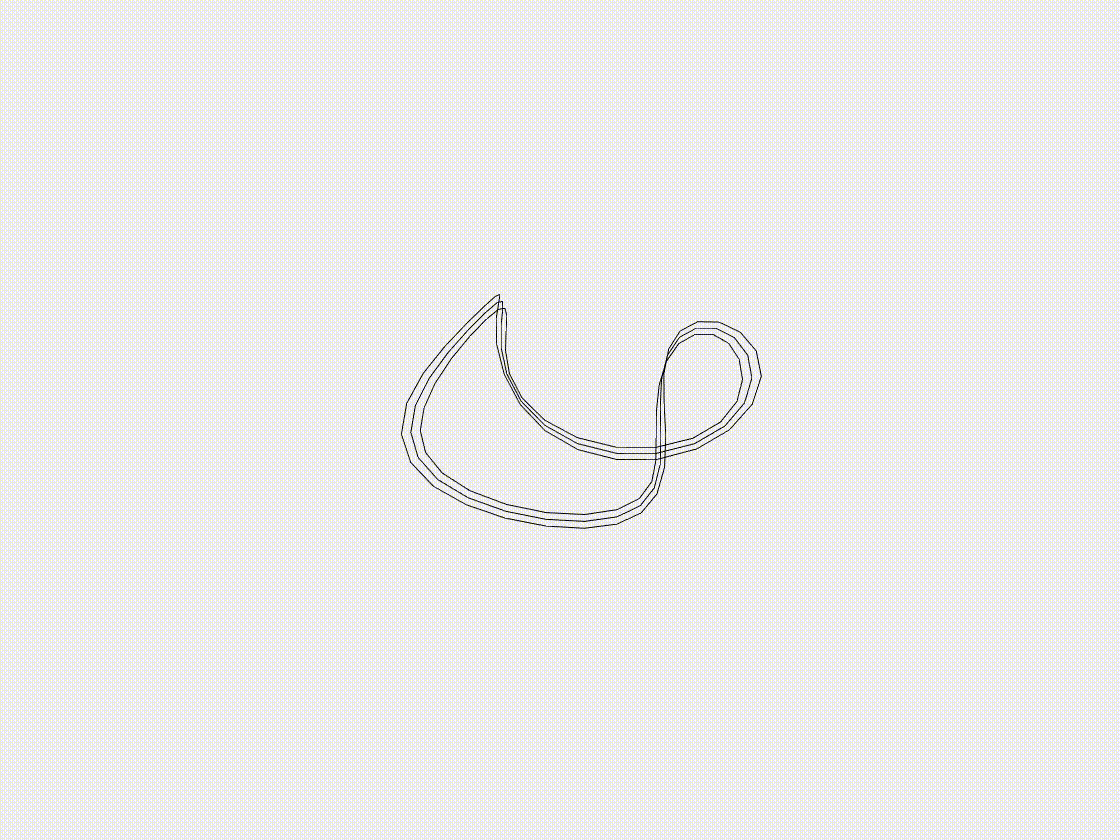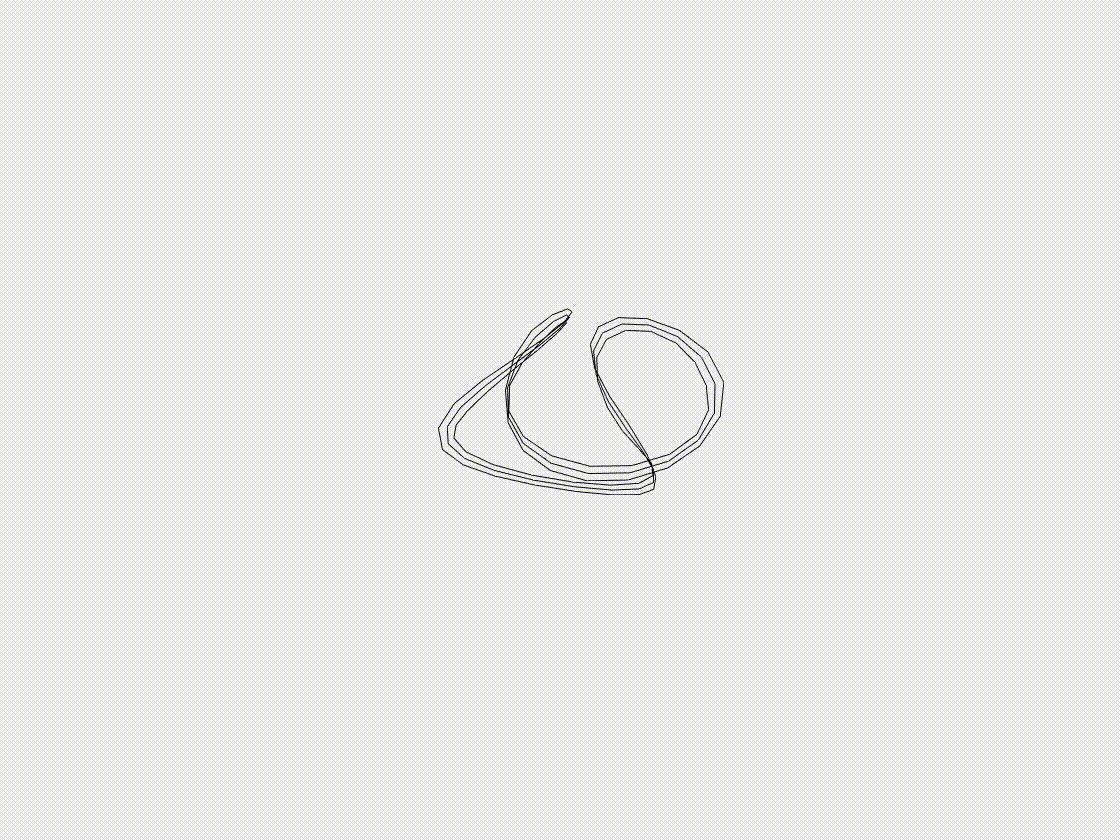
Growth of annular ribbon
Growth ribbons are usually built as a model for plant tissues in nature, such as the swelling and shrinkage of pine cones, pea pods and leaves, during these processes the ribbons usually have a large deformation behavior. In this case study, we examine the growth of an annular ribbon, driven by an increase in its natural curvature. The ribbon is initially defined with a specified radius and undergoes deformation as its natural curvature increases, mimicking the behavior of plant tissues. We track the ribbon’s deformation throughout the growth process, focusing on the resulting structural changes. This case highlights the ability of the DDG model to accurately simulate complex growth behaviors and large deformations in soft, thin structures.
Simulation Initialization
To initialize the simulation, the following inputs are used:
- Geometry and connection:
- (i) Nodal positions: the position of the nodes, \(\mathbf{q}(t=0)\), with a total of \(N=40\). The system is initialized as an annular ribbon connected end to end with a radius \(R = 1.0\mathrm{~m}\).
- (ii) Stretching elements: connection of every two consecutive nodes, with a total of \(N_{s}=40\).
- (iii) Bending elements: connection of every two consecutive edges, with a total of \(N_{b}=40\).
- Physical parameters:
- (i) Young’s modulus, \(E=10.0\mathrm{~MPa}\).
- (ii) Poisson’s ratio, \(\nu=0.5\).
- (iii) Material density, \(\rho=100\mathrm{~kg/m^3}\).
- (iv) Ribbon width \(w=0.2\mathrm{~m}\), ribbon thickness is \(h=0.01\mathrm{~m}\), thus \(EI_{2} = Ewh^3/12\), \(EI_{1} = 400EI_{2}\), and \(GJ=Gwh^3/3\).
- (v) Damping viscosity, \(\mu = 0.1\).
- (vi) Gravitational field, \(\mathbf{g}=[0.1,0.1,0.1]^{T}\mathrm{~m/s^2}\).
- (vii) The overall simulation is static, i.e., \(\mathrm{ifStatic} = 1\).
- Numerical parameters:
- (i) Total simulation time, \(T=25.0\mathrm{~s}\).
- (ii) Time step size, \(\mathrm{dt} =0.001\mathrm{~s}\).
- (iii) Numerical force tolerance, \(\mathrm{tol}=1\times 10^{-4}\).
- (iv) Maximum iterations, \(N_{\mathrm{iter}}=10\).
- Boundary conditions:
- Based on the symmetry, the \(Y\) and \(Z\) displacements of two points where the diameter intersects the annulus ribbon is constrained, while the \(X\) and \(Z\) displacements of another two points where the other perpendicular diameter intersects the annulus ribbon are constrained, thus the constrained array, \(\mathcal{FIX} = [2,3,31,33,62,63,91,93]^{T}\).
- Initial conditions:
- (i) Initial position is input from the nodal positions.
- (ii) Initial velocity is set to zeros for all nodes.
- Loading steps:
- (i) Perturbation step: a small perturbation to the initial horizontal configuration is created by applying a small gravitational force (with \(\mathbf{g}=[0.1,0.1,0.1]^T\mathrm{~m/s^2}\)) when \(t \le 1.0\mathrm{~s}\).
- (ii) Growth step: when \(t>1.0\mathrm{~s}\), the normalized natural curvature, \(\bar{\kappa}_1 / l\), would increase with a growth rate \(\dot{\bar{\kappa}}_1 / l=0.01 \mathrm{~s^{-1}}\).
Dynamic Rendering